Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio Formula Example Calculation Explanation
For example, a cyclical company can have a low fixed asset turnover during its quiet season but a high one in its peak season. Hence, the best way to assess this metric is to compare it to the industry mean. At the company level, internal factors can influence asset turnover ratio. One of the prime drivers is how efficient a company is in maximizing their assets and managing inventory. The type of industry a company operates in affects its asset turnover ratio.
Accelerated Depreciation
Remember we always use the net PPL by subtracting the depreciation from gross PPL. Since using the gross equipment values would be misleading, we always use the net asset value that’s reported on the balance sheet by subtracting the accumulated depreciation from the gross. Companies with seasonal or cyclical sales patterns may show worse ratios during slow periods.

Can the fixed asset turnover be negative?
The asset turnover ratio measures how effectively a company uses its assets to generate revenues or sales. The ratio compares the dollar amount of sales or revenues to the company’s total assets to measure the efficiency of the company’s operations. To calculate the ratio, divide net sales or revenues by average total assets. The fixed asset turnover ratio measures a company’s efficiency and evaluates it as a return on its investment in fixed assets such as property, plants, and equipment. In other words, it assesses the ability of a company to generate net sales from its machines and equipment efficiently.
What Does an Asset Turnover of 1 Mean?
As each industry has its own characteristics, favorable asset turnover ratio calculations will vary from sector to sector. Companies can artificially inflate their asset turnover ratio by selling off assets. This improves the company’s asset turnover ratio in the short term as revenue (the numerator) increases as the company’s assets (the denominator) decrease. However, the company then has fewer resources to generate sales in the future.
- Below we describe the fixed Fixed Asset Turnover definition, explain how you can calculate it, and finally, how to use it to grow your business.
- Therefore, it is important to analyze the ratio in the context of your own company’s history and goals.
- Asset turnover ratio results that are higher indicate a company is better at moving products to generate revenue.
- The Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio measures the efficiency at which a company is capable of utilizing its long-term fixed asset base (PP&E) to generate revenue.
To stay on top of profitability, they will assess ways to improve efficiency, reduce costs, incentivize employees and optimize operations to maximize the bottom line. Understanding your Fixed Asset Turnover can be a cornerstone in your strategic planning. A high ratio could indicate that your current assets are being utilized to their fullest, signalling that it might be a good time to expand. Conversely, a low ratio could mean it’s time to reassess and refine your current strategies before taking on more.
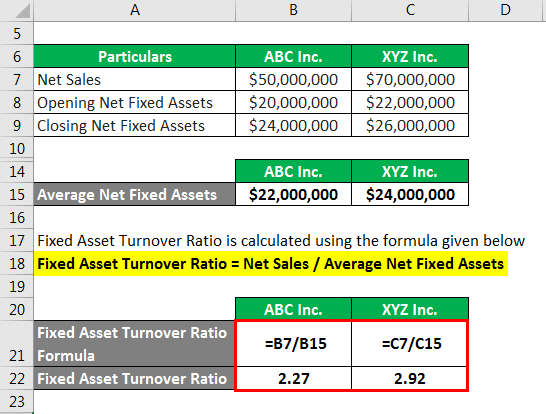
Generally, a greater fixed-asset turnover ratio is more desireable as it suggests the company is much more efficient in turning its investment in fixed assets into revenue. In general, the higher the fixed asset turnover ratio, the better, as the company is implied to be generating more revenue per dollar of long-term assets owned. An increase in the ratio over previous periods can, on the other hand, suggest the company is successfully turning its investment in its fixed assets into revenue. Therefore, XYZ Inc.’s fixed asset turnover ratio is higher than that of ABC Inc. which indicates that XYZ Inc. was more effective in the use of its fixed assets during 2019. As technology continues to advance and markets evolve, the fixed asset turnover ratio is likely to become an even more critical metric for companies across a range of industries.
A corporate insider has access to more detailed information about the usage of specific fixed assets, and so would be less inclined to employ this ratio. The asset turnover ratio is used to evaluate how efficiently a company is using its assets to drive sales. It can be used to compare how a company is performing compared to what are building automation systems bas its competitors, the rest of the industry, or its past performance. A higher FAT ratio indicates that a company is effectively utilizing its fixed assets to generate sales, showcasing management’s efficiency in asset utilization. The asset turnover ratio uses the value of a company’s assets in the denominator of the formula.
The working capital ratio measures how well a company uses its financing from working capital to generate sales or revenue. Thus, it helps to assess how well the company’s long term investments are able to bring adequate returns for the business. The asset turnover ratio measures the efficiency of a company’s assets in generating revenue or sales.
For example, an e-commerce company may use a fulfillment service (link) instead of its warehouse. The turnover metric falls short, however, in being distorted by significant one-time capital expenditures (Capex) and asset sales. GOBankingRates’ editorial team is committed to bringing you unbiased reviews and information. We use data-driven methodologies to evaluate financial products and services – our reviews and ratings are not influenced by advertisers.
Different industries have varying levels of capital intensity, which directly impacts how assets are used to drive revenue. The fixed asset turnover ratio is similar to the tangible asset ratio, which does not include the net cost of intangible assets in the denominator. Asset turnover ratio results that are higher indicate a company is better at moving products to generate revenue.
A ratio that is declining can indicate that the company is potentially over-investing in property, plant or equipment or simply producing a product that isn’t selling. BNR Company builds small airplanes and has net sales of $900,000 for the year using equipment that cost $500,000. So take all Fixed Assets less any accumulated depreciation they may have generated and then divide the result into net sales. This is an advanced guide on how to calculate Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio with detailed analysis, example, and interpretation. Some methods of depreciation can produce a book value that is false, and thus the performance will look much better than reality.



